Understanding Friction Between Solid Objects: Factors That Affect Resistance to Motion
- By admin --
- Saturday, 18 Mar, 2023
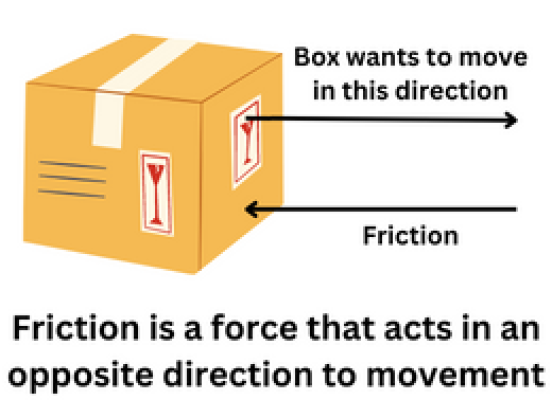
The friction between two solid objects is affected by several factors, including:
1. Surface roughness:
The rougher the surfaces in contact, the greater the friction between them. Rough surfaces have more peaks and valleys, which increase the contact area between the two objects. This increases the friction because there are more points of contact between the surfaces.
2. Surface area:
The greater the surface area in contact between two objects, the greater the friction. The greater the surface area in contact, the greater the friction. This is because more of the surfaces are in contact with each other, which creates more resistance to motion.
3. Normal force:
The greater the normal force (the force pressing the two objects together), the greater the friction. The normal force is the force pressing the two objects together. The greater the normal force, the greater the friction. This is because the objects are being pressed more tightly together, which creates more resistance to motion.
4. Type of materials:
The nature of the materials in contact also affects the friction. For example, rubber on concrete has more friction than steel on ice. The nature of the materials in contact can greatly affect the friction between them. Some materials have rougher surfaces, which create more friction, while others are smoother and create less friction. Additionally, the coefficient of friction, which is a measure of the friction between two materials, can vary greatly depending on the materials in contact.
5. Temperature:
Changes in temperature can also affect the friction between two surfaces. Generally, an increase in temperature can reduce friction. Changes in temperature can affect the friction between two surfaces. When two surfaces rub against each other, they generate heat due to friction. This heat can cause the surfaces to expand, which can reduce the contact area between the surfaces and therefore reduce friction. Additionally, some materials can become more or less viscous at different temperatures, which can also affect the friction.
6. Lubrication:
The presence of a lubricant between two surfaces can reduce friction. The presence of a lubricant between two surfaces can greatly reduce friction. Lubricants fill in the gaps between two surfaces and create a smooth layer, which allows the surfaces to slide past each other more easily.
7. Velocity:
The speed at which the two objects are moving relative to each other can also affect friction. At low speeds, friction may increase, while at high speeds, it may decrease. The speed at which the two objects are moving relative to each other can also affect friction. At low speeds, friction may increase because there is more time for the surfaces to come into contact with each other. At high speeds, however, friction may decrease because the surfaces don't have as much time to interact with each other.
8. Pressure:
Pressure can affect the friction between two surfaces. Higher pressure can increase friction, while lower pressure can reduce it. Pressure can also affect the friction between two surfaces. When the pressure between two surfaces is increased, the surfaces are pressed more tightly together, which creates more resistance to motion and therefore increases friction. When pressure is decreased, the surfaces are pressed less tightly together, which reduces resistance to motion and therefore reduces friction.
Overall, it's important to consider all of these factors when trying to understand the friction between two solid objects. The interactions between these factors can be complex, and it's often necessary to perform experiments or simulations to get a more complete understanding of the situation.